In this blog, we will look in-depth at DeFi, a decentralised financial system powered by blockchain technology. We will examine the fundamental features of DeFi networks, network fees, the coins used, key differences from centralised finance (CeFi), and the advantages and disadvantages from a technical perspective.
How DeFi Works?
DeFi (Decentralized Finance) is a financial system powered by blockchain technology that offers an alternative to the traditional financial system (CeFi). It enables users to transact directly with each other without relying on a central authority. To start with DeFi, you need to create a cryptocurrency wallet and purchase cryptocurrency. Then, you can connect to your chosen DeFi platform and perform various financial transactions.
- Smart Contracts: DeFi transactions are managed by smart contracts, which are automated programs that trigger specific actions when predefined conditions are met. This allows for reliable and transparent execution of money transfers, lending, borrowing, and other financial activities.
- Blockchain: DeFi networks record transactions on a public ledger (blockchain), making all transactions transparent and traceable.
- Cryptocurrencies: Various cryptocurrencies are used in DeFi networks to conduct transactions and transfer value. The most commonly used cryptocurrencies include Ethereum (ETH), stablecoins, and governance tokens.
Coins Used in DeFi Networks
DeFi networks utilize various cryptocurrencies. The most commonly used coins are:
- Ethereum (ETH): The most popular token in the DeFi ecosystem. Many DeFi protocols operate on the Ethereum blockchain.
- Stablecoins: Cryptocurrencies pegged to a stable asset like the US Dollar. They are widely used in DeFi lending and borrowing protocols.
- Governance Tokens: Some DeFi protocols offer governance tokens that grant users the right to participate in the platform’s governance.
Key Features of DeFi Networks
Decentralization:
The most significant feature of DeFi is its ability to execute transactions securely and transparently without relying on a central authority. In traditional financial systems, central authorities such as intermediary institutions and banks play a role, whereas in DeFi, this role is undertaken by blockchain technology. This eliminates the risk of a single point of failure and gives users more control over their funds.
Transparency:
All transactions in DeFi networks are public and traceable on the blockchain. This ensures that all transactions are transparent and auditable, addressing the issue of privacy and accountability that exists in traditional financial systems.
Accessibility:
Anyone with an internet connection anywhere in the world can access DeFi networks. This provides inclusive financial services to those who have limited access to the traditional financial system. Without the need for a geographic location or a bank account, anyone can use DeFi platforms to perform financial transactions.
Security:
DeFi networks are protected by cryptographic encryption and robust blockchain technology. This offers a higher level of security compared to traditional financial systems. DeFi networks are more resistant to fraud and cyber-attacks, playing a crucial role in safeguarding users’ funds.
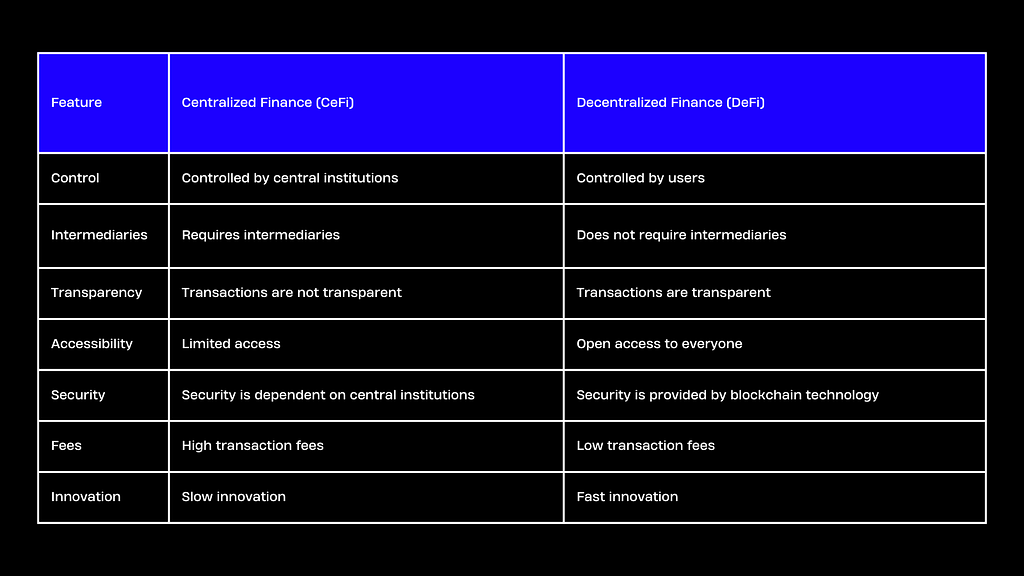
Differences Between Centralized and Decentralized Finance
Advantages of DeFi:
- Decentralization: DeFi operates without any central authority. This allows users to have more control over their funds and financial transactions.
- Transparency: All transactions are recorded on a public ledger, ensuring transparency and accountability in the financial system.
- Accessibility: Anyone with an internet connection can access DeFi networks, providing inclusive financial services to those with limited access to the traditional financial system.
- Security: DeFi networks offer a higher level of security through cryptographic encryption and robust blockchain technology.
- Low Fees: Transaction fees in DeFi networks are generally lower compared to traditional financial institutions.
- Rapid Innovation: DeFi’s decentralized nature allows for faster innovation compared to traditional financial systems.
Disadvantages of DeFi:
- Complexity: DeFi networks and smart contracts can be complex and challenging for beginners to understand.
- Security Risks: Like any new technology, DeFi networks have security risks. Errors or flaws in smart contracts can lead to loss of funds.
- Volatility: Cryptocurrencies are highly volatile, making DeFi investments risky.
- Regulations: DeFi is still an emerging field with uncertain legal regulations, creating uncertainty for investors.
