In cryptocurrency trading, the two primary order types are market orders and limit orders. These orders serve different strategies based on speed, price control, and risk. In this blog, we’ll cover the details of how these orders work, how they appear on the order book, and answer frequently asked questions.
What is a Market Order?
A market order is executed immediately at the current market price. Traders use market orders when they want to buy or sell quickly, accepting the best available price in the market.
• Advantages: Transactions are fast, ideal for highly volatile markets.
• Disadvantages: There is a risk of slippage, meaning the trade may be completed at a price higher or lower than expected.
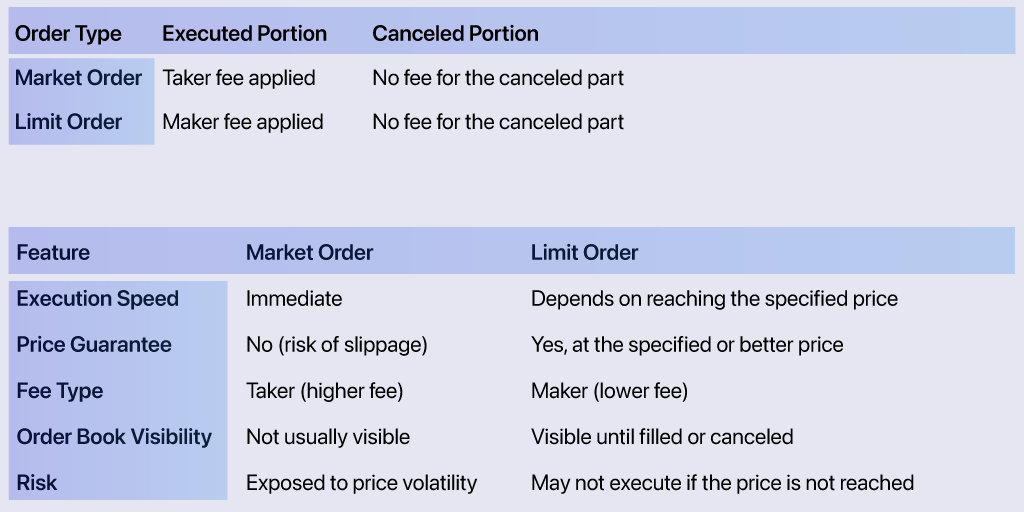
• Commission: Market orders incur a taker fee, which is typically higher since they remove liquidity from the market.
Example: If Bitcoin is priced at $27,000, and you place a market order to buy 2 BTC, the order might execute like this:
- 1 BTC at $27,000
- 0.5 BTC at $27,100
- 0.5 BTC at $27,200
Here, the purchase is fulfilled in portions at different prices, depending on available market liquidity.
What is a Limit Order?
A limit order allows traders to set a specific price at which they want to buy or sell. The trade will only be executed if the market reaches the specified price or better.
• Advantages: Traders have control over the price at which they buy or sell.
• Disadvantages: If the market does not reach the desired price, the order remains unfilled.
• Commission: Limit orders usually incur a maker fee, which is lower since they add liquidity to the market.
Example: If Bitcoin is trading at $27,000, and you place a limit buy order at $26,500, the order will remain open until the price drops to $26,500. If the price doesn’t reach that level, the order will stay in the order book or remain unexecuted.
How Market and Limit Orders Appear on the Order Book?
- Market Orders:
Market orders are typically not visible on the order book because they are executed instantly. However:
If Liquidity is Insufficient: The order may only be partially executed, with the remaining portion visible on the order book.
In High Volatility: Market orders may appear briefly on the book due to delays in execution.
- Limit Orders:
Limit orders remain visible on the order book until executed or canceled. Orders are prioritized on a first-come, first-served basis at the same price level.
What Happens When a Partially Filled Order is Canceled?
For Market Orders:
Market orders are executed immediately, and the completed portion cannot be canceled. If part of the order remains unfilled due to insufficient liquidity, you can cancel the remaining amount without incurring additional fees.
Example: You place a market buy order for 2 BTC, but only 1.5 BTC is filled. If you cancel the remaining 0.5 BTC, no fee will be charged for the unfilled portion.
For Limit Orders:
When canceling a limit order, only the unfilled portion is removed from the order book. The completed portion is irreversible, and the corresponding maker fee is charged.
Example: You place a limit sell order for 2 BTC at $27,000. If 1 BTC sells, you can cancel the remaining 1 BTC without any fee for the canceled portion. However, the 1 BTC already sold will incur the maker fee.
When Should You Use Each Order Type?
In Volatile Markets: Use a market order to quickly enter or exit a position when prices are fluctuating rapidly.
For Precise Pricing: Use a limit order when you want to control the exact price at which your trade is executed.
Market and limit orders serve different strategic purposes in cryptocurrency trading. Market orders are ideal for fast execution but come with higher taker fees and the risk of slippage. Limit orders provide better price control with lower maker fees but may remain unexecuted if the market doesn’t reach the desired price. When canceling orders, fees only apply to the executed portions, and the unfilled parts are canceled without charge. Knowing how and when to use these orders will help traders navigate the crypto market more effectively.
